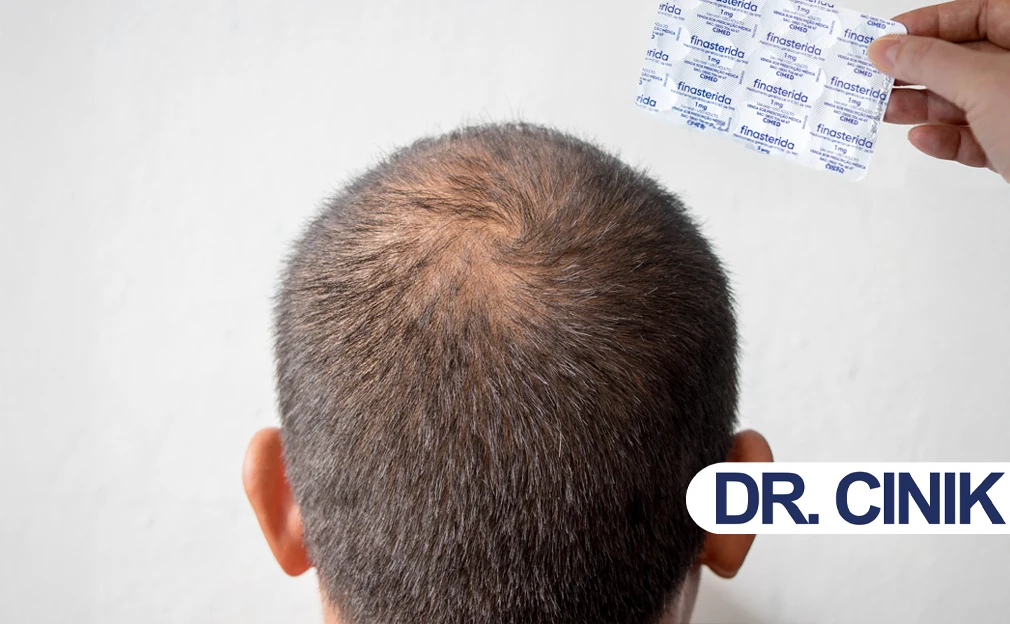
Finasteride is one of the most frequently prescribed treatments used in male-pattern baldness and mild prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor, Finasteride lowers the levels of dihydrotestosterone, or DHT, hormones responsible for hair loss and enlargement of the prostate. The drug works well, yet it often finds itself unjustifiably surrounded by myths and concerns regarding possible side effects.
The article Finasteride’s Side Effects: Between Truths and Myths addresses several aspects related to Finasteride, including its benefits, who should take it, those who need to avoid it, and how it should be taken. Whether you are weighing the pros and cons of Finasteride or have already decided to use the drug, keep reading to make an informed choice.
What Is Finasteride and What Is It Used for?
Finasteride, commonly used for treating enlarged prostates, is also usually prescribed for male-pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). Growing clinical evidence has proved its effectiveness in helping reduce further hair thinning and its potential to initiate its growth. It is usually indicated for adult men suffering from gradual hair loss at the crown or top of the head.
The vast majority of individuals will begin to see visible differences after a few months of use, with most of them considered an improvement after six months to a year of use. In clinical studies, Finasteride has been shown to retain and regrow hair better in individuals using it for a prolonged period as opposed to those not taking the medication.
Finasteride is FDA-approved for the treatment of male-pattern hair loss and is usually considered a first-line treatment. It is a prescription medication that is not indicated for use in females and children.
How Does Finasteride Work?
Before addressing how Finasteride works, let’s first get to the root of the problem by breaking down how male pattern baldness happens.
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness, is the most common type of hair loss in men. It typically starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the top of the head, and is usually caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, most notably, a hormone called DHT.
DHT, a derivative of testosterone, causes the gradual shrinking of the hair follicles on the scalp in some individuals. As this happens, hair becomes softer and shorter, until it eventually stops growing altogether.
Finasteride works by reducing the level of DHT in your body by 66%. It inhibits the action of an enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT, which helps prevent further hair loss and, in most cases, promotes hair regrowth. Most men notice a significant difference after taking it consistently for a few months.
In short, DHT shrinks your hair follicles, leading to male pattern baldness, and Finasteride helps by blocking DHT, allowing your hair to grow thicker, longer, and healthier.
4 Finasteride Benefits
Here are 4 benefits of Finasteride that were clinically proven:
- Cholesterol reduction: According to a study conducted at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, users of Finasteride have, on average, at least 30 points lower cholesterol than non-users.
- AtherosclerosisAtherosclerosis is the thickening or hardening of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of... prevention: Significantly high dosages of Finasteride in mice prevented the process of atherosclerosis from happening and decreased inflammation in the liver.
- Reduction of cardiovascular-related issues: Finasteride may even lower the scope of cardiovascular issues due to reduced cholesterol levels and blockage in arteries.
- Hair loss treatment: Finasteride also has a lot to do with preventing hair loss, apart from being a well-known treatment for cases like male pattern baldness and enlarged prostate.
Types of Finasteride
Finasteride is available in oral and topical formulations—oral works systemically and may have more side effects, while topical acts locally on the scalp with typically fewer side effects; effectiveness depends on individual needs.
Oral Finasteride
Oral finasteride works throughout the entire body to reduce DHT and prevent hair loss when taken in tablet form. However, because it has a systemic effect, it may cause side effects such as sexual dysfunction.
Topical Finasteride
Topical Finasteride, in contrast, is applied directly to the scalp, acts locally, and tends to result in fewer systemic side effects. Both forms can support hair regrowth, but the choice between them should be based on individual needs and how well each option is tolerated.
How Should You Take Finasteride?
It’s essential to know that using Finasteride to treat male pattern hair loss may take at least until the third month before you notice any real improvement. Hair loss and subsequent regrowth usually occur gradually and not all at once. Most users who respond positively to the medication will, however, see changes on average within the first 12 months of use. If you have consistently used Finasteride for a full year without evidence of improvement, chances are low that it will help if you continue using it.
Finasteride is effective only while you are taking it. It slows hair fall and may promote growth, but these effects are not permanent. Once you stop Finasteride, any new hairs gained will usually shed within 12 months, and hair loss will likely resume soon after. For the best results, users should take the medication consistently, even after they see good results, to avoid reversing any progress.
According to Dr. Emrah Cinik, our hair transplantHair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves the extraction of hair follicles from a designated donor site, followed by... expert at Dr. Cinik, “Individual responses to Finasteride tend to vary. Factors such as age, the extent of hair loss, and the timing of starting the treatment affect how well it works.”
How Long Should You Take Finasteride for?
To see effective results, Finasteride has to be taken every day for at least three months before most patients notice that their hair loss has stopped or that new hair is growing. Controlled clinical data for treatment beyond 12 months do not exist. It likely requires indefinite use to maintain the benefits.
Who Can Take Finasteride?
Those who can take Finasteride are the following categories:
- Men over 18 experiencing male-pattern baldness: By blocking DHT, the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles, Finasteride helps reduce baldness.
- Men suffering from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): It decreases the size of the prostate, thereby relieving symptoms such as increased frequency and urgency of urination.
- Non-allergic individuals and those who do not suffer from liver disease.
Can Women With Hair Loss Use Finasteride?
Although Finasteride is not indicated for treating hair loss in women, in some cases, it may be prescribed off-label to women after menopause by certain doctors.
Why Women Can’t Take Finasteride?
While Finasteride is prescribed for men, it is generally contraindicated in women who are pregnant or likely to become pregnant. This is because it could affect the development of the male fetus and potentially cause birth defects in the genitalia.
Weighing in on this point, Dr. Cinik cautions that “For women who could be pregnant, Finasteride may alter hormonal levels and disrupt the menstrual cycle. Women experiencing hair loss should consult a healthcare provider for alternatives that might be safer.”
How Long Does It Take Finasteride to Work for Hair Loss?
Studies show that following the use of Finasteride, DHT levels drop by approximately 65% within the first 24 hours after the first dose.
While DHT drops quickly, it will take months for any hair regrowth to be seen. Clinical research shows:
- Some individuals see results after about 3 months of treatment.
- More discernible results tend to show up after about 5-6 months or 12 months.
- Long-term studies imply that continued Finasteride use can lead to results, even if changes are not noticeable in the early stages.
Finasteride Dosage
Since Finasteride is available in oral and topical forms, each has a specific dosage regimen that is adaptable for safe and efficient usage.
Oral Finasteride
Finasteride is usually taken in a dose of one tablet of 1 mg once a day for the treatment of male pattern baldness. Results may take at least three months to become apparent. Consistent use is necessary to maintain hair regrowth. After treatment has been stopped, new hair most likely will be lost within a year.
Topical Finasteride:
Usually, topical Finasteride is applied at least once or twice a day on the scalp using a dropper or spray, but only under the guidance of a healthcare practitioner. The amount and frequency can vary depending on the formulation and patient needs. With your fingers, spread evenly over the balding areas.
It’s worth noting that you must not use oral and topical Finasteride simultaneously without the advice of a health professional, as it may result in dosage exceeding normal levels, leading to a higher risk of side effects.
What Should I Do If I Forget a Finasteride Dose?
In case you missed a Finasteride dose, skip it and continue with your regular dosing schedule. It is not advised to make up for the missed dose by taking two doses at once.
What Should I Do If I Overdose on Finasteride?
If you feel you have overdosed on Finasteride, get medical assistance right away. If the victim collapses, has a seizure, trouble breathing, or can’t be awakened, get emergency medical attention right away.
Finasteride’s Side Effects: Between Truths and Myths
The common side effects of Finasteride are:
- Decrease in libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Ejaculation issues
- Breast enlargement and tenderness
- Skin rash
If mild, these effects may disappear within a few days or weeks. If they are persistent or severe, consult your physician or pharmacist.
Plus, Finasteride may cause severe allergic reactions. Thus, discontinue the use of the product and seek immediate medical assistance if the allergic reaction is suspected, accompanied by any of the following symptoms:
- Difficulty in breathing or wheezing
- Heart palpitations
- Feverishness or malaise
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat
- Difficulty swallowing or constriction of the throat
- Itching, skin rash, and pale red bumps on the skin (hives)
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness, feeling faint, or fainting
- Abdominal cramps
- Joint pain
Finasteride can also cause suicidal thoughts and depression in a smaller number of patients.
Dutasteride vs Finasteride Side Effects
Finasteride and Dutasteride may potentially cause sexually related side effects like reduced libido and erectile dysfunction. These are generally mild and resolve after discontinuation of the drug. Some might say that Dutasteride has fewer sexual side effects, but it also may bring about breast tenderness/enlargement. Pregnant women must not handle either drug because of the potential birth defects they may cause.
Read more: Dutasteride for Hair Loss: How Well Does It Work?
How to Reduce Side Effects of Finasteride?
As we’ve learned previously, Finasteride indeed has some common and adverse effects; however, there are easy ways to make the treatment more comfortable and diminish the likelihood of side effects:
Go topical with Finasteride
Research suggests that 1 mg of Finasteride is adequate for treating male pattern baldness and may also have fewer side effects than 5 mg Finasteride. Keep taking the medication as directed by your trichologist, and do not compensate for a missed dose by taking two doses the next time.
Stay positive
A meta-analysis of more than 60,000 patients showed that sexual side effects were reported at nearly the same rate in both the Finasteride and placebo groups, with only about 1% more in those who actually took Finasteride, suggesting a likely nocebo effect.
Healthy living
Healthy habits such as cessation of smoking and maintenance of a healthy diet with exercise and low-stress levels can support the body and assist in the reduction of side effects.
Consultation
Psychotherapy is not limited to mental health; it can be of assistance when it comes to libido, anxiety, and serious worries about Finasteride side effects.
Does Microdosing on Finasteride Help?
Lower doses of Finasteride — often called microdosing — are becoming more popular for treating hair loss. Even at just 0.2 mg, studies show it can cut DHT levels in half, which is usually enough to help slow down hair thinning.
The main reason people choose microdosing is to reduce the risk of side effects, especially sexual ones. While it may not be as strong as the standard 1 mg dose, it can still be very effective for those with mild or early-stage hair loss, or for anyone concerned about how their body might react.
Finasteride and Pregnancy
As we have mentioned above, due to the potential risks it poses to a developing fetus, Finasteride is strictly contraindicated during pregnancy. High-quality studies indicate that exposure to the drug can lead to serious birth defects, particularly affecting the development of the male reproductive system when taken during pregnancy with a male fetus.
Finasteride Alternatives
When it comes to treating male pattern baldness, several options are available, each targeting different aspects of hair loss and offering varying levels of effectiveness.
Dutasteride vs Finasteride
Male-pattern baldness can be treated with two DHT blockers: Dutasteride and Finasteride, each differing widely in potency and approval status. Finasteride is FDA-approved for hair loss and inhibits one type of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, meanwhile, Dutasteride is not FDA-approved for hair loss and inhibits both types, thus being more potent.
Studies indicate that for advanced cases of hair loss, Dutasteride is the better option; however, the side effects they have regarding sexuality are mild and reversible in both cases. The choice depends on hair loss severity, response to treatment, and the physician’s directives.
Minoxidil vs Finasteride
The two treatments that have been clinically approved for male pattern baldness are Minoxidil and Finasteride; nevertheless, they act through entirely different modalities. Minoxidil stimulates hair growth by expanding blood vessels, increasing blood flow to the follicles, and ultimately producing thicker hair at a faster growth rate. It promotes regrowth in areas where hair has thinned, but it does not prevent further hair loss.
Finasteride reduces the level of DHT, a male hormone that shrinks hair follicles and causes baldness. This reduction occurs through inhibition of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone to DHT. Therefore, it is possible that the dual treatment may yield improved results for some individuals, as these treatments act on different aspects of the hair loss process.
Minoxidil and Finasteride Topical Solution
The combination of Minoxidil and Finasteride topical treatments can be effective for hair loss. Minoxidil stimulates hair growth by improving circulation to the scalp, while Finasteride acts on DHT, which causes hair loss. Therefore, in cases of advanced hair thinning, better results may be attained through the combined use of both drugs.
Plus, the topical formulas may minimize systemic side effects compared to oral preparations, and, hence, their regular use with careful observation for irritations is essential. Always consult your physician before starting this combined treatment to ensure its appropriateness for you.
Learn more: How Long Does Minoxidil Take to Work?
Final Thoughts on Finasteride’s Side Effects: Between Truths and Myths
Though Finasteride has clear benefits in treating male-pattern baldness and benign prostate hyperplasia, one must consider possible severe side effects, usually not permanent. The key to managing the side effects of Finasteride is to understand its mechanism of action and realize that the positives may outweigh any risks while keeping in mind the actual truths and myths regarding its use.
Although with proper guidance and monitoring a lot of patients may use Finasteride in a safe, effective manner for hair loss or prostate issues, this article: Finasteride’s Side Effects: Between Truths and Myths, emphasizes that given your overall health and specific therapeutic needs, you have to consult with a physician to decide whether Finasteride is the right medication for you.
FAQs
What Does Finasteride Do?
Finasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor that works by blocking a male hormone responsible for prostate enlargement and hair loss, helping treat both BPH and male pattern baldness.
Is Finasteride Safe?
Finasteride can usually be safely taken for long periods of time. For many months or even years, many take the pill without any complications.
Are Finasteride Side Effects Permanent?
Finasteride side effects are typically not permanent, but the risk of experiencing longer-lasting effects may increase with extended use of the medication.
Does Finasteride Regrow Hair?
Yes. Studies show Finasteride does not simply limit and slow hair loss, Finasteride also works to promote hair regrowth. However, your hair regrowth success depends on a few factors, including the location of your hair loss on your scalp.
Does Finasteride Grow Hair in Completely Bald Men?
There is no clinical data available for completely bald men.
Can Finasteride Be Used by Elderly Men?
No clinical trials have been conducted on the use of finasteride for treating male pattern hair loss in men over the age of 41.
What Should You Avoid While Taking Finasteride?
Don’t share Finasteride with another person, even if they have the same symptoms you may have.
What Other Drugs Will Affect Finasteride?
Finasteride may interact with other medications, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Be sure to inform your doctor about everything you are taking