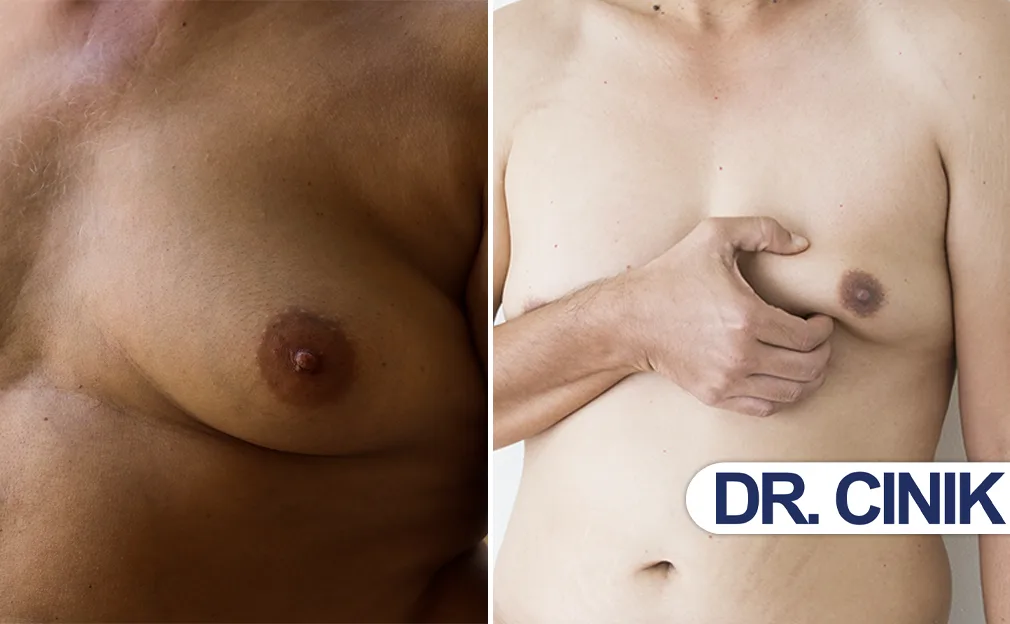
If you’ve ever looked in the mirror and thought, “Hmm, is my chest puffier than usual?”, you’re not alone. It’s a question many guys (and even some teens and older men) have asked themselves at some point. Is it just moobs (chest fat), or is it gynecomastia, a condition that occurs due to hormone imbalance? And most importantly, how can you tell the difference and what to do in either case?
Well, don’t worry. We’ve got your back (and your chest) covered.
Chest Fat vs. Gynecomastia: What’s the Difference?
Before we get into symptoms and signs, let’s start with the basics. Both gynecomastia and chest fat can give you that “man boobs” look, but the causes and treatments are quite different.
Chest Fat (Pseudogynecomastia, or Adipomastia)
This is just what it sounds like: fat that collects in the chest area. It’s more common in overweight individuals, but it can happen to lean guys too, especially if genetics aren’t on their side. This isn’t a medical condition per se; it’s simply fat deposition, just like belly or love handles.
Gynecomastia
Unlike chest fat, gynecomastia is a medical condition that results in enlargement of male breast gland tissue. This is not only fat, but also actual glandular growth, often triggered by imbalance of hormones. Estrogen (yes, men have it too) starts playing a bigger role than testosterone, and breast tissue starts to grow.
So how do you figure out which one you’ve got?
The ‘Do I Have Moobs or Gyno?’ Guide
Still not sure what you’re dealing with? Here’s a quick self-assessment checklist to help.
Step 1: The Pinch Test
Use your thumb and forefinger to gently pinch around the nipple area. If it feels firm or rubbery directly behind the nipple, that could be glandular tissue (gynecomastia). If it just feels like soft fat and you can pinch it easily, it’s likely chest fat.
Step 2: Check for Tenderness
Is it sore or sensitive to touch? Gynecomastia is often painful; chest fat rarely is.
Step 3: Look at the Rest of Your Body
Do you carry extra fat elsewhere (belly, love handles, thighs)? Then it’s more likely chest fat. If your body is lean but your chest is puffy, that leans more toward gynecomastia.
Step 4: When Did It Start?
Did it begin during puberty? Pubertal gynecomastia is quite common and usually fades within a couple of years. Did it appear later in life, or after taking a new medication? That’s worth paying attention to.
Step 5: Visit a Doctor (Seriously)
We love self-diagnosis as much as the next guy, but nothing beats a medical opinion. If you’re unsure, a doctor can do a physical exam or even order an ultrasound to be 100% certain.
What Causes Chest Fat?
Chest fat is typically a result of:
- Eating too much and exercising too little (sounds pretty obvious, right?)
- Genetics (some people store fat in different places, and that’s hereditary)
- Hormonal imbalances, although less severe than in case of gynecomastia
Unfortunately, you can’t spot-reduce fat, but a calorie-controlled diet and regular strength training will help trim things down.
Some men are pre-disposed to fat buildup in the chest zone. You could be ripped in the arms and legs but still soft up top. Blame evolution or your parents, whichever feels better.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia has a few more causes. It’s all about hormones.
The most common ones include:
- Puberty: Hormone fluctuations during teenage years can cause temporary gynecomastia.
- Aging: As testosterone levels naturally drop, estrogen may start to have more influence.
- Medications: Anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, antidepressants, and even heartburn meds can be culprits.
- Substances: Alcohol, marijuana, and certain street drugs can mess with hormones.
- Medical conditions: Liver or kidney disease, tumors, and thyroid problems can also trigger gynecomastia.
Basically, if your hormones get out of whack, breast tissue can grow. And once it’s there, it rarely shrinks back down on its own.
Treatment: Chest Fat vs. Gynecomastia
Treating Chest Fat
Good news: chest fat can be burned off with a mix of:
- Regular cardio and strength training
- A clean, balanced diet
- Overall fat loss
Best exercises include push-ups, bench presses, cable crossovers, and HIIT workouts. But remember: your body decides where to lose fat first, not you. Be patient.
Treating Gynecomastia
Now here’s where things differ.
Mild cases during puberty often resolve on their own within a few years. But if it’s persistent or causing emotional distress, there are other options:
- Medication: Hormone therapy may help in early stages, but it’s not a sure thing.
- Surgery: The most effective treatment is male breast reduction surgery. It removes both glandular tissue and excess fat for a flatter, firmer chest.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Quitting drugs, limiting alcohol, and reviewing your meds with a doctor can prevent progression.
Gynecomastia doesn’t respond well to diet and exercise alone. If it’s truly glandular, no amount of bench pressing will flatten it out completely.
So, What Should You Do?
First off, don’t panic. Whether it’s chest fat or gynecomastia, both conditions are treatable.
Here’s your action plan:
- Assess your symptoms: Use the signs, pinch test, and tenderness guide.
- Check your lifestyle: Are you eating well, exercising, and managing stress?
- Get a doctor’s opinion: Especially if the tissue is hard, painful, or grew all of a sudden.
- Make a plan: For chest fat, hit the gym. For gynecomastia, consider talking to a specialist.
A Final Word
Gynecomastia and chest fat can look similar, but they’re not the same. One is a fat issue, the other is glandular. Both are treatable. What matters most is understanding your body and knowing when to ask for help. If in doubt, talk to a doctor (not just the internet).
All in all, knowledge is power… and sometimes, the first step to a better t-shirt fit.
Read more: Thinking About Gynecomastia Surgery in Turkey? Here’s the Cost Breakdown
FAQs
Q: Can gynecomastia go away on its own?
A: Yes, especially in teens. But if it sticks around for more than two years, it’s likely permanent without treatment.
Q: Can I get rid of gynecomastia with push-ups?
A: Sadly, no. Exercise can build chest muscles and reduce fat, but it won’t eliminate glandular tissue.
Q: Is surgery for gynecomastia safe?
A: Yes, especially when performed by a board-certified plastic surgeon. Recovery is usually smooth, and results can be life-changing.
Q: Is gynecomastia common?
A: It’s very common. About 60% of men develop gynecomastia at some point in their lives.
Q: Can skinny guys have gynecomastia?
A: Absolutely. Gynecomastia is about hormones, not just fat. Even bodybuilders can have what’s known as bodybuilder gyno.