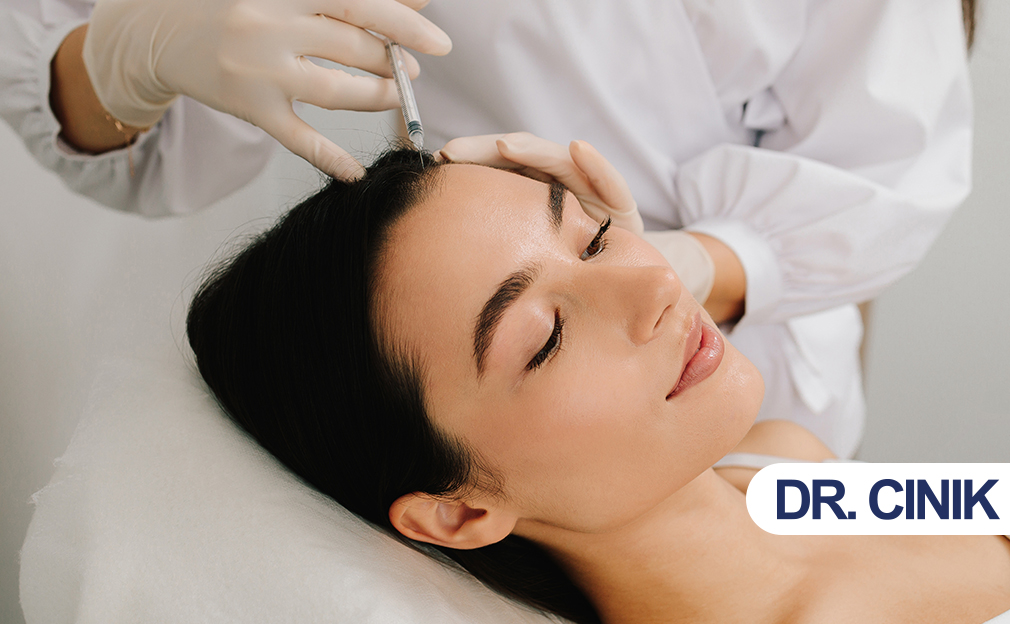
Hair mesotherapy is a non-surgical treatment that involves injecting small amounts of vitamins, amino acids, minerals, vasodilators, and sometimes medications directly into the scalp to support hair follicles and improve circulation. By delivering substances straight to the mid-layer of the skin, mesotherapy aims to nourish follicles more effectively than topical treatments while limiting systemic side effects.
Clinical observations suggest mesotherapy may be helpful for people with androgenetic alopecia and certain types of non-scarring hair loss, particularly when hair loss is recent. Some studies report improved tolerance and patient satisfaction compared with topical treatments, and combinations with PRP or dutasteride have shown promising results, especially in female-pattern hair loss. However, overall scientific evidence remains limited and not fully conclusive.
The treatment typically involves short sessions of superficial microinjections performed over several weeks, with possible maintenance treatments later. Side effects are generally mild and temporary, such as tenderness, swelling, or itching. Mesotherapy is not suitable for everyone, including pregnant women, smokers, and individuals with certain medical conditions or medications, making consultation with an experienced clinician essential.
While mesotherapy can be considered as a supportive or complementary option, established treatments such as topical minoxidil, oral finasteride or dutasteride, PRP, and hair transplantation have stronger evidence for long-term effectiveness. Decisions should be individualized and guided by professional medical advice.
1. What is mesotherapy for hair
Quick Answer: Mesotherapy for hair is a minimally invasive treatment in which vitamins, amino acids, and medications are injected into the scalp to improve blood flow, nourish hair follicles, and support hair growth, with generally mild side effects.
Mesotherapy is a medical technique in which a clinician injects small amounts of medication, vitamins, hormones, or enzymes into the mesoderm, or middle layer of skin. A hair-mesotherapy solution typically contains vasodilators, vitamins, amino acids, and minerals. These ingredients can improve blood flow to the scalp, nourish hair follicles, and strengthen hair. Mesotherapy with a solution containing dutasteride and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has shown effectiveness and comfort for hair loss, particularly in female-pattern hair loss (A Nagaja et al., 2024). Compared with topical minoxidil, mesotherapy with nutritional supplements appears more effective, better tolerated, and requires fewer treatment sessions. The shorter the duration of male-pattern hair loss, the better the response to mesotherapy. Adverse effects are minimal and may include minor headaches and pain at the injection sites. A regional nerve block can be used to reduce discomfort during the procedure (Mammucari et al., 2012).
1.1. How mesotherapy works for hair growth
Quick Answer: Mesotherapy stimulates hair growth by delivering nutrients and medications directly to hair follicles, improving scalp health with minimal side effects.
Mesotherapy treats hair loss by injecting substances into the scalp. The injections can stimulate hair regrowth. The substances usually contain vitamins, amino acids, minerals, and sometimes medications. Mesotherapy aims to enhance the hair and scalp condition and nourish hair follicles (M Aledani et al., 2024). Injections deliver drugs directly to the follicles. This reduces possible side effects. Mesotherapy is safer, less invasive, and more effective than some alternatives. Mesotherapy with platelet-rich plasma is also available. Mesotherapy has a high patient satisfaction rate.
1.2. What the treatment involves
Quick Answer: Hair mesotherapy involves superficial scalp injections of nutrients and medications to improve circulation and support hair regrowth.
Hair mesotherapy is a non-surgical method in which vitamins, minerals, medications, and biological substances are injected into the scalp to stimulate hair regrowth and prevent hair loss. This technique is designed to help people with hair loss resulting from poor blood and nutrient supply to the hair follicles.
Hair mesotherapy is increasingly gaining acceptance as a mesotherapeutic option for treating hair loss, primarily androgenetic alopecia. Mesotherapy facilitates the administration of drugs directly to the target area, ensuring higher local concentrations with fewer systemic side effects compared to systemic delivery. The physiological benefit of mesotherapy lies in its capacity to promote skin rejuvenation and improve local circulation (A Nagaja et al., 2024).
During mesotherapy sessions, a series of superficial microinjections are performed on specific scalp areas to deliver micronutrients essential for healthy hair. Various hair-loss treatments are administered together with mesotherapy. These include vasodilators and growth factors. Mesotherapy improves the penetration of these drugs into the scalp, offering multiple treatment benefits (M Aledani et al., 2024).
2. Is mesotherapy effective for hair growth
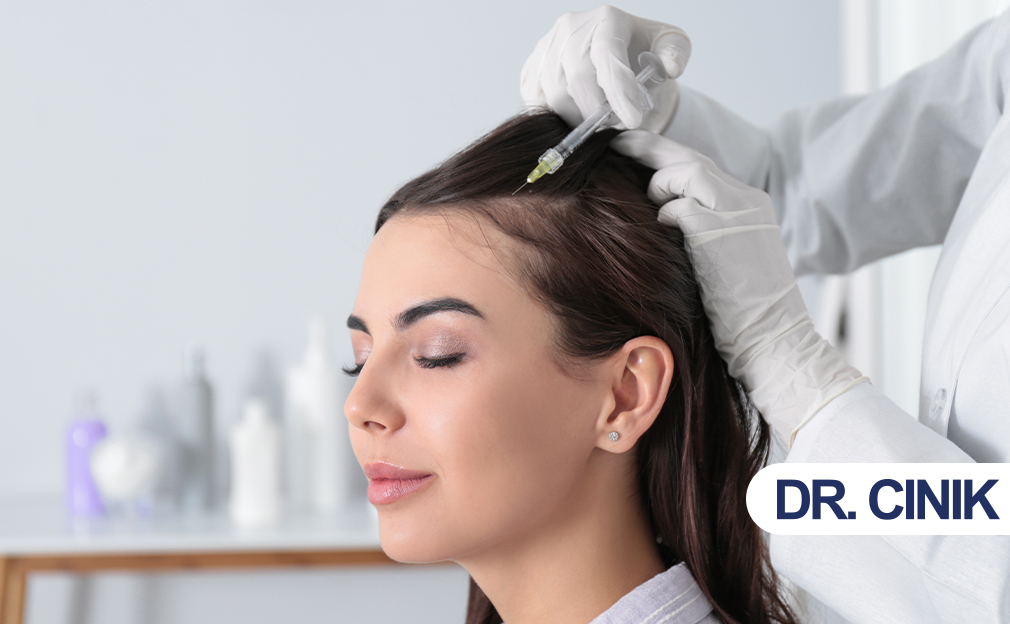

Quick Answer: Mesotherapy may help with hair growth by delivering nutrients directly to hair follicles, showing promising results, especially in female-pattern hair loss, but overall scientific evidence remains limited.
Various scientific analyses show mesotherapy can be beneficial for hair loss, though the evidence is not conclusive (M Aledani et al., 2024). Men and women seeking an effective treatment for thinning hair often consider products that promote circulation or stimulate the scalp. These amounts are more difficult to achieve with topical agents that do not penetrate the epidermis. Mesotherapy, which delivers small amounts of drugs into the mid-layer of the skin, has been integrated into some aesthetic practices. The superficial administration in mesotherapy results in better delivery to the target area, lower doses, and fewer side effects than systemic administration. Satisfactory results with minimal side effects have been observed for combined protocols involving mesotherapy and topical or intralesional therapies, which can extend a treatment’s benefits after initial care has stopped. Mesotherapy combined with dutasteride has shown safety and effectiveness for female pattern hair loss, offering a better, quicker response. The technique is considered more practical and acceptable than topical minoxidil for this condition (A Nagaja et al., 2024).
3. Who can consider mesotherapy
Quick Answer: Mesotherapy may suit people with androgenetic or temporary hair loss and should be evaluated by a clinician.
Certain groups of people are more likely to benefit from mesotherapy than others. Patients with androgenetic alopecia are good candidates. People experiencing sudden hair loss from trauma, illness, or stress may also be able to benefit. Scarring and other forms of alopecia are different; they do not improve with mesotherapy because they do not involve hair follicles.
The injections deliver nutrients, amino acids, vitamins, and other substances directly into the scalp, where they can have a local effect. Microneedling may deliver some benefit through increased absorption of topical medications applied around the same time. Mesotherapy candidates should review their background and past restoration treatments with their clinician. Some patients also consider platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments or oral medications, including finasteride and dutasteride. (A Nagaja et al., 2024)
3.1. Who should avoid it
Quick Answer: Mesotherapy should be avoided by pregnant women, smokers, and people with certain medical conditions or medications, and suitability must be assessed by a clinician.
Some people may not be good candidates for mesotherapy. Pregnant women, smokers, people taking certain drugs or supplements, and people with certain health problems should not have this treatment.
Pregnant women should avoid mesotherapy. This treatment is unlikely to help with pregnancy-related hair loss. Women remain good candidates if they stop breast-feeding (M Aledani et al., 2024).
Drinking coffee before a mesotherapy session can trigger a reaction. Stopping coffee for a few hours before treatment may improve the results.
Smokers may not get satisfactory results with mesotherapy, though there is no research confirming this.
Some drugs, supplements, and health issues can also pose problems. Anti-depressants and steroids, blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs, high blood pressure and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer, allergies, and skin, liver, and kidney diseases may prevent candidates from having mesotherapy.
3.2. How to talk to a clinician
Quick Answer: Discuss mesotherapy with an experienced hair-loss clinician, prepare your concerns in advance, and review qualifications and options before deciding on treatment.
Describing mesotherapy as an essential therapy for hair loss stimulates the interest of people and pushes them to look for additional information. They explore how the therapy works, whether it is effective, who may benefit, and what to expect. The next step includes discussing the treatment with a clinician experienced in hair loss solutions. A clinician can recommend the best options tailored to concerns and goals.
Finding the right clinician can take time. Recommendations from trusted friends or family might help. Searching online with terms such as “mesotherapy,” “hair loss,” or “scalp” along with the name of the city or region can provide a relevant list of experts. Checking qualifications and reviewing testimonials can help identify the right fit. When ready to meet a clinician, it may help to prepare a brief description of concerns and areas to address. Openly discussing concerns does not require prior knowledge. It can be beneficial to receive clear answers to basic questions and to explore a range of options before committing to any treatment. (Zerbinati et al., 2021)
4. What to expect during and after treatment
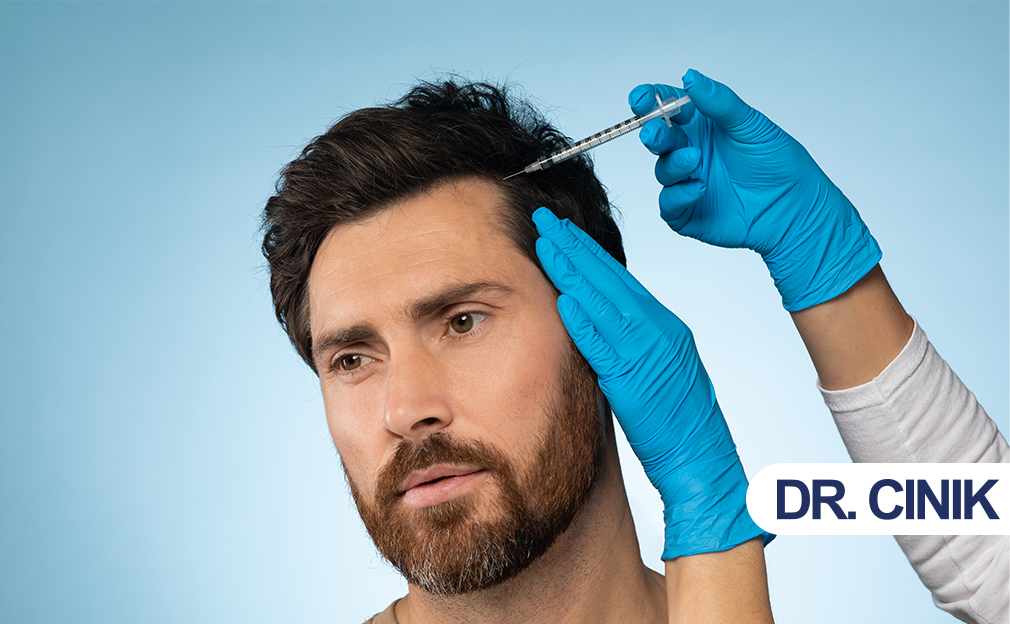

Quick Answer: Hair mesotherapy sessions last about 20–30 minutes, involve mild anesthesiaEnsuring Comfort During Hair Transplants Sedation is used in hair transplantation to help patients remain calm and comfortable throughout the..., and are done over several weeks; side effects are usually mild, and aftercare includes avoiding washing, heat, hats, and intense activity for 1–3 days.
Mesotherapy sessions for hair treatment usually take 20 to 30 minutes. Clinicians generally administer two types of anesthesia: a topical cream and extra small injections of a dilute local anesthetic. Topical treatments do not always completely suppress discomfort and pain levels depend on how sensitive individuals are. Protocols vary by clinician, but hair mesotherapy typically takes place every 15 days for 4 sessions, then monthly for 4 additional sessions. After this, some patients request maintenance as needed.
Potential side effects of hair mesotherapy include
- tenderness
- mild swelling
- itchiness
- rash
- headache
- dizziness.
It is unclear whether the injected substances, the needling alone, or some combination triggers these effects. Most patients tolerate the procedure well, notwithstanding these concerns.
After mesotherapy, it is important to follow some guidelines to promote optimal recovery. The clinician will share specific recommendations, but some general care measures are beneficial for almost everyone.
Do not wash the hair for 24 hours after the mesotherapy session.
Some people are advised to wait longer, especially those with oily hair (48 hours). For those who need to wash their hair sooner, some products are more suitable. The expert should confirm those.
Avoid exposing the scalp to heat.
Avoid hair dryers, hair irons, styling products, sauna or steam bath, swimming pool, and sun exposure for 48 hours.
Avoid aggressive hair treatments.
Chemical treatments (permanents, dyes) and physical treatments (straightening, curling) should be deferred for at least a week (ideally two).
Avoid wearing hats.
Avoid sports for 48-72 hours.
Some sports increase blood circulation, resulting in enhanced product diffusion. High-impact activities that promote excessive sweating should be avoided for the same reason. (Zerbinati et al., 2021)
5. What are the alternatives and next steps?
Quick Answer: Minoxidil and finasteride are first-line treatments, with PRP or hair transplant as alternatives if needed.
Mesotherapy is a medical procedure that introduces drugs, vitamins, and minerals into the skin. It aims to treat different health problems, including hair loss. But the evidence supporting mesotherapy for hair growth is weak.
People looking to address hair thinning or baldness might consider medicines. These include the for topical minoxidil and the oral finasteride. These treatments have more evidence of effectiveness than mesotherapy. Medication is a good first step for most people. If these options do not work or unwanted side effects occur, other procedures can be considered. These include platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and scalp micropigmentation, as well as surgical hair transplant (A Nagaja et al., 2024) ; (M Aledani et al., 2024).
5.1. What are other hair growth options?
Quick Answer: Other hair growth options include topical minoxidil, PRP, low-level laser therapy, botanical products, and oral finasteride or dutasteride, with treatment choice guided by a clinician.
Many treatments encourage hair growth. Mesotherapy is one option. Most solutions contain blood flow promoters, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and compounds supporting strong, healthy hair. Such treatments may complement steroid injections.
Topical minoxidil is the most established alternative. Despite some reports of paradoxical hair loss, mesotherapy with dutasteride offered women a less invasive, comfortable approach. Compared to minoxidil and mesotherapy with nutritional supplements, combinatory regimens involving dutasteride were the least effective and poorly tolerated (A Nagaja et al., 2024).
Other options include botanical products, low-level laser therapy, platelet-rich plasma, and finasteride or dutasteride (M Aledani et al., 2024). Consult a clinician to further explore mesotherapy or other treatments.
6. What is the cost of Mesotherapy?
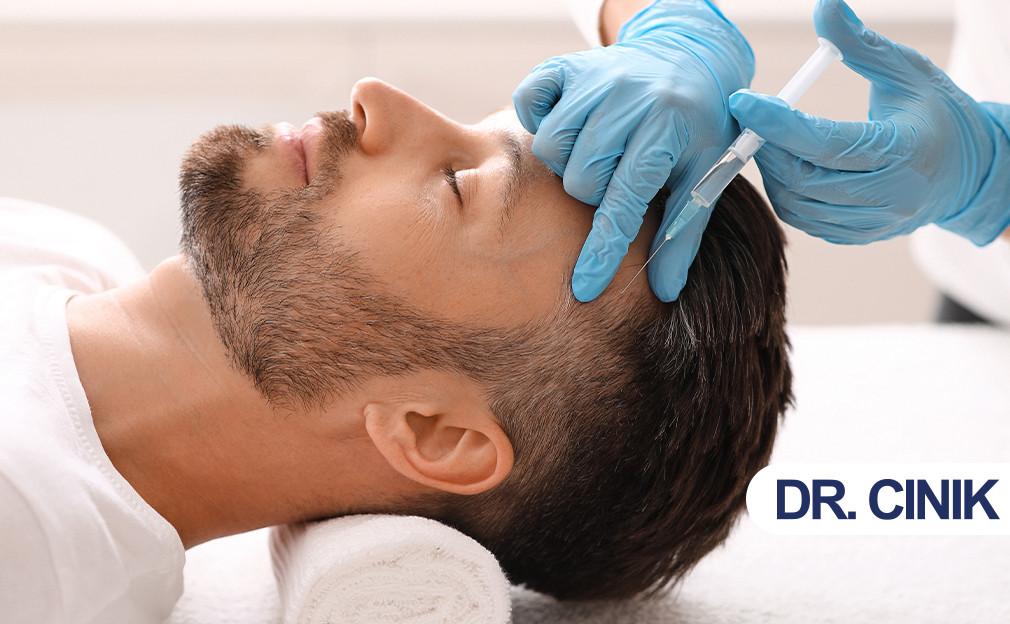

Quick Answer: Hair mesotherapy typically costs $45–$500 per session, depending on the country and clinic.
The cost of hair mesotherapy varies widely depending on the country, clinic expertise, and whether treatments are purchased individually or as part of a package. Below are typical per-session price ranges across popular treatment destinations:
- Turkey: $100 – $300 USD
- United Kingdom: £150 – £400 GBP
- United States: $200 – $500 USD
7. Conclusion
Mesotherapy aims to treat the underlying cause of problems rather than the effects. It has been used for hair regrowth since the early 2000s and is recommended as a solution against hair thinning. The drug used is rich in vitamins, amino acids, antioxidants and antiandrogens. It improves blood circulation, prevents hair loss and stimulates hair regeneration. Hair regrowth generally occurs in between 3 and 6 sessions. The combination of mesotherapy and antioxidants, vitamin D and biotin gives promising results. The safety and efficacy of the treatment for hair regrowth have not been established yet (A Nagaja et al., 2024).
References:
A Nagaja, S., S John, R., P Kumar, S., and Krishnan, M. “Comparison of the Efficacy of Two Different Local Anesthesia Techniques for Mesotherapy in Temporal Region Alopecia.” 2024. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Mammucari, M., Gatti, A., Maggiori, S., and F. Sabato, A. “Role of Mesotherapy in Musculoskeletal Pain: Opinions from the Italian Society of Mesotherapy.” 2012. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
M Aledani, E., Kaur, H., Kasapoglu, M., Yadavalli, R., Nawaz, S., Althwanay, A., and Sankar Nath, T. “Mesotherapy as a Promising Alternative to Minoxidil for Androgenetic Alopecia: A Systematic Review.” 2024. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Zerbinati, N., Sommatis, S., Maccario, C., Chiara Capillo, M., Di Francesco, S., Rauso, R., Protasoni, M., D’Este, E., Dalla Gasperina, D., and Mocchi, R. “In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of a Not Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel on Human Keratinocytes for Mesotherapy.” 2021. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov